HIGHLIGHTS
- In a bariatric population, more than 90% of the patients presented with histopathological steatosis and some degree of fibrosis, whereas over 20% had active NASH.
- FIB-4 score had high overall accuracy in assessing the presence of advanced liver fibrosis in individuals with obesity.
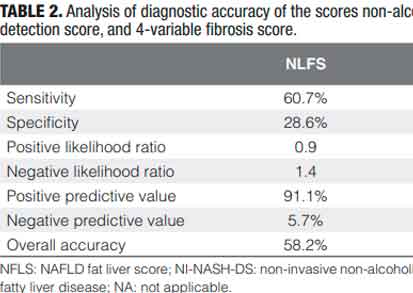
- NFLS score was moderately accurate for the assessment of hepatic steatosis in individuals with obesity.
- NI-NASH-DS was moderately accurate for the assessment of NASH in individuals with obesity.
ABSTRACT – Background –
Non-invasive markers have been developed to assess the presence and severity of liver abnormalities related to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Objective – To analyze the diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive NAFLD markers (NAFLD liver fat score [NLFS], noninvasive non-alcoholic steatohepatitis detection score [NI-NASH-DS] and f ibrosis score based on four variables [FIB-4]) in individuals with obesity undergoing bariatric surgery. Methods – A descriptive retrospective crosssectional study was carried out enrolling 91 individuals who underwent bariatric surgery at a tertiary-level public university hospital. Non-invasive NAFLD markers were calculated using laboratory tests, clinical and anthropometric variables and diagnostic accuracy tests were calculated comparing them in relation to the gold-standard test for this analysis (histopathological evaluation). Results – A total of 85.7% of the participants were female and mean age was 39.1±9.8 years. The average body mass index was 38.4±3.6 kg/m2. At histopathological examination, 84 (92.3%) patients presented with steatosis, 82 (90.1%) with some type of fibrosis; 21 (23.1%) patients were diagnosed with NASH according to the NAFLD activity score criteria. The overall accuracy of NLFS score was 58.2% for general hepatic steatosis and 61.5% for moderate to severe steatosis. The overall accuracy of FIB-4 was 95.4% for advanced fibrosis. NI-NASH-DS had a 74.7% overall accuracy for NASH. Conclusion – In a population of individuals with obesity, the FIB-4 score had high overall accuracy in assessing the presence of advanced liver fibrosis, whereas the NFLS and NI-NASH-DS had moderate accuracies for the assessment of steatosis and NASH, respectively. Keywords – Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; obesity; liver function tests; fatty liver; biomarkers.
AUTORES
Gustavo Macedo HADDAD1, Martinho Antonio GESTIC2, Murillo Pimentel UTRINI2, Felipe David Mendonça CHAIM2, Elinton Adami CHAIM2 and Everton CAZZO2.