HIGHLIGHTS
- Failure to clear bile duct stones in the index ERCP can be seen in 15–20% of cases, and identifying the factors associated with failure is important.
- A prospective analysis was conducted to identify and analyze the factors that could predict the failure of complete CBD clearance.
- The present study reported a successful clearance of CBD stones during the index procedure in only 70% of patients.
- A stone diameter ≥15 mm, location of stones in hepatic ducts, presence of stricture distal to stone, and impacted stone were independent predictors of failed bile duct clearance.
ABSTRACT – Background –
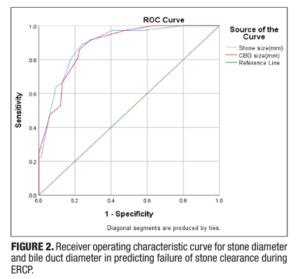
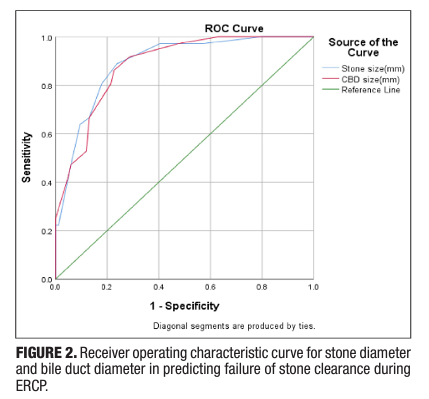
Common bile duct (CBD) stones are known to complicate 10–15% of gallstone diseases. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is the therapeutic modality of choice for bile duct clearance in CBD stones but may fail to achieve stone clearance. Objective – This prospective study was done to identify the predictors of failure of CBD clearance with ERCP. Methods – All consecutive patients with bile duct stones undergoing ERCP at a tertiary care center were prospectively included from October 2020 to October 2021. The study’s primary outcome was to identify and analyze factors that could predict the failure of complete CBD clearance. Results – A total of 120 patients (50.8% males, median age: 53.5 years) were included in the final analysis. Successful clearance of CBD stones during the index procedure was achieved in 70% of patients. At a cut-off stone diameter of >10.5 mm and CBD diameter of >12.5 mm, the AUC was 0.890 and 0.884, respectively, to predict failed clearance of CBD. On multivariate analysis, stone diameter ≥15 mm [odds ratio (OR) 16.97, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.629–176.785], location of stones in hepatic ducts (OR 7.74, 95%CI: 2.041–29.332), presence of stricture distal to stone (OR 6.99, 95%CI: 1.402–34.726) and impacted stone (OR 21.61, 95%CI: 1.84–253.058) were independent predictors of failed bile duct clearance. Conclusion – Stone size and location are independent predictors of failed bile duct clearance. The endoscopist should consider these factors while subjecting a patient to biliary ductal clearance to plan additional intervention.
AUTORES
Abhishek KAMUNI, Lohith KUMAR, Suprabhat GIRI, Sumaswi ANGADI, Sunil Kumar NANJEGOWDA and Sukanya BHRUGUMALLA.