HIGHLIGHTS
- Pulmonary function, respiratory muscle strength, and mobility can predict operative safety and determine the timing of hospital discharge.
- Our results indicate a reduction in these variables post-operatively and at discharge compared to pre-operative assessment, with the exception of the Tiffeneau index.
- The role of physiotherapy in the prevention and rehabilitation of these patients should be strongly considered.
ABSTRACT – Background
Several preoperative pulmonary assessment protocols have been established over the years, but assessments of this magnitude are lacking in the bariatric population. Therefore, the assessment of lung capacity, maximum inspiratory and expiratory pressures, the peak expiratory flow and mobility can be predictors of operative safety and determine the time of hospital discharge.
Objective: To evaluate lung capacity, respiratory muscle strength and level of mobility in the pre, immediate post-operative and hospital discharge of patients undergoing bariatric surgery.
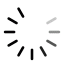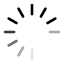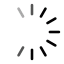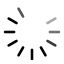
Methods: Cross-sectional study, with 38 bariatric patients undergoing surgical intervention. Anthropometric data, lung function, respiratory muscle strength and mobility level were evaluated pre-, post-operatively and at hospital discharge. Statistical Analysis: GEE; P<0.05.
Results: In relation to the preoperative period, in the POi there was a significant reduction in mobility, respiratory muscle strength, FVC, FEV1, PEF and a significant increase in these variables at hospital discharge, however, not reaching the same conditions as the preoperative period, except the Tiffeneau index (P<0.644).
Conclusion: Bariatric surgery impacts the mobility, respiratory muscle strength and lung function of patients with grade II and III obesity, leading to longer hospital stays and possible major complications. The role of physiotherapy in the prevention and rehabilitation of these patients must be strongly considered.
AUTORES
ROSSI, Danusa STEDILE, Ney Ricardo de Alencastro SILVA, Elias Aguiar da GASPERI, Danielly de NETO SANTOS, Luciano EIBEL, Bruna