HIGHLIGHTS
- Chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine (CS/GlcN) preparation was analyzed for structure.
- CS/GlcN reduced histological score and macrophage infiltration.
- CS/GlcN decreased MMP-9 activity and NO production.
- CS/GlcN not cytotoxic in the intestinal epithelial cells.
ABSTRACT – Background
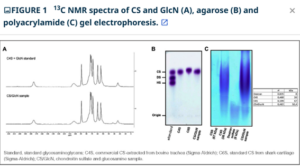
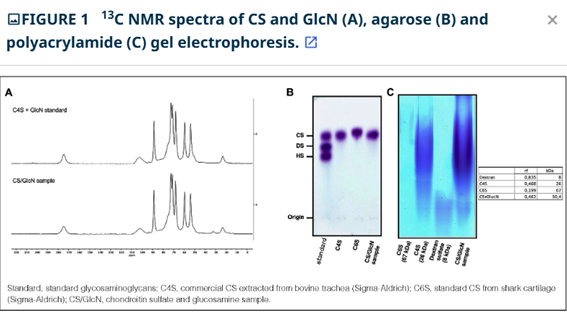
Chondroitin sulfate (CS) and glucosamine (GlcN) are indicated for the treatment of some inflammatory diseases, such as osteoarthritis, mainly because of the anti-inflammatory effects in reducing metalloproteinases activities (MMP), and other inflammatory mediators. Herein, we reported the structure of the CS, the anti-inflammatory and protective effects of the CS, and GlcN administration in ulcerative colitis model induced by dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) in rats. Experimental data indicated that CS disaccharide composition is very similar to the C4S standard, with modal molecular weight at 30.4 kDa. Orally administration of the CS/GlcN improved the severity of acute colitis with reduction the histological score and goblet cells destruction. We also observed a decreasing in NO production, myeloperoxidase and MMP, especially MMP-9, activities. Moreover, CS/GlcN not cytotoxic in the intestinal epithelial cells. These results indicate that combination CS/GlcN showed improvements in intestinal inflammation and protection intestinal barrier, suggesting CS/GlcN might have beneficial effects in treatment of IBD.
AUTORES
OLIVEIRA, Luiz Gustavo de CARPANEZ, Arthur Girardi SILVA, João Victor Gerheim da CASTAÑON, Maria Christina Marques Nogueira CHEBLI, Julio Maria Fonseca AGUIAR, Jair Adriano Kopke de