HIGHLIGHTS
- The dynamics of research collaboration in hepatology were analyzed over 30 years (1994-2023), focusing on co-authorship networks.
- The author employed the powerful tool of Python to analyze 9,278 hepatology-related publications, ensuring the assessment of macro-level indicators and micro-level metrics was precise and reliable.
- Increased network fragmentation, with components rising from 338 (1994-2003) to 1,302 (2014-2023).
- Consistently low network density were found, indicating limited direct collaboration. High clustering coefficients suggest collaborations occur within tightly connected groups.
- Despite significant growth in publications, collaboration in hepatology remains localized and fragmented.
ABSTRACT – Background
This study aims to analyze the structural dynamics of research collaboration in hepatology over a 30-year period (1994-2023), focusing on co-authorship networks. By examining data from the Web of Science Core Collection, the study explores key metrics such as network density, clustering coefficient, and centrality measures, providing insights into how collaborative efforts have shaped the field of hepatology.
Methods: Using Python (Version 3.10.5) in the PyCharm environment, I conducted a network analysis of 9,278 hepatology-related publications. Macro-level indicators, including network density, clustering coefficient, number of components, and average path length, were used to evaluate overall network structure. Micro-level metrics, such as degree centrality, closeness centrality, and betweenness centrality, were employed to assess the influence of individual researchers within the network.
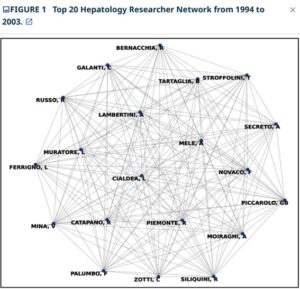
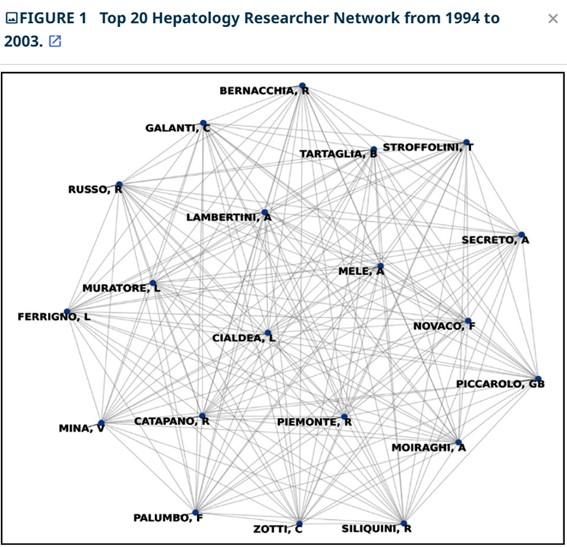
Results: The analysis showed an increase in network fragmentation, with components rising from 338 in 1994-2003 to 1,302 by 2014-2023. Despite the growing number of publications, network density remained consistently low, indicating limited direct collaboration. However, high clustering coefficients across all periods suggest that collaborations form in tightly connected groups. This study identified key researchers such as LAMBERTINI A. (1994-2003), Manns, Michael P. (2004-2013), and Berg, Thomas (2014-2023), who played central roles, linking different research clusters and facilitating collaboration across groups.
Conclusion: Hepatology research has experienced significant growth in publications over the past 30 years, yet collaborative efforts remain localized, with increasing network fragmentation. Identifying central researchers who bridge gaps between otherwise disconnected groups is essential to fostering broader collaboration. This analysis underscores the importance of strengthening international cooperation and collaborative research to address the increasingly complex and region-specific liver diseases worldwide.
AUTORES
OGASAWARA, Naruaki