HIGHLIGHTS
- Acute pancreatitis following pancreatic surgery can lead to serious complications.
- The authors investigated whether prolonged fasting affects the severity of acute pancreatitis in an experimental model.
- Prolonged fasting exacerbated pancreatic enzyme levels increased inflammatory cytokines, liver oxidative stress and pancreatic necrosis.
ABSTRACT – Background –
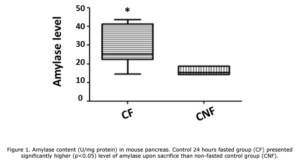
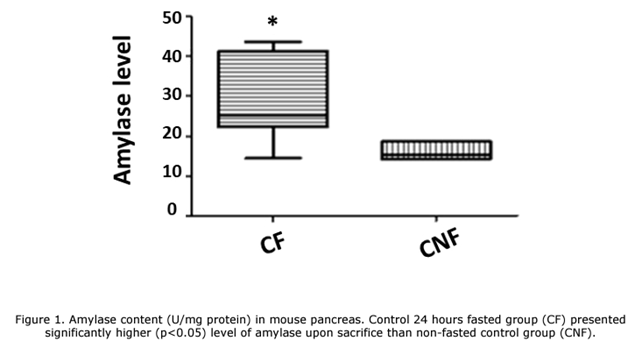
Acute pancreatitis following surgical or endoscopic procedures on the pancreas can compromise the outcome and lead to severe complications and even death. The aim of this study was to determine whether prolonged fasting affects the severity of acute pancreatitis (AP). Methods – Male mice were divided into 4 groups: Group CF (n=5) control animals that fasted for 24 hours; Group CNF (n=5) control animals that did not fast; Group APF (n=7) that fasted for 24 hours and underwent induction of acute pancreatitis (AP) and Group APNF (n=7) that did not fast and underwent AP. Eight hours after AP blood was collected for evaluation of cytokines: IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α and MCP-1. Liver tissue was collected for determination of Malondialdehyde, pancreatic tissue for determination of enzyme content and lung tissue for determination of myeloperoxidase. Results – Significant increase in pancreatic amylase content was observed in group CF and increased serum levels of IL -6, Il-10 and MCP-1 were in group APF. Liver malondialdehyde was also increased in APF animals. APF group showed much more necrosis of the pancreatic acinar cells. Conclusion – In the present study, we observed an increase in the severity of acute pancreatitis with prolonged fasting in a severe acute pancreatitis model. These results suggest that in clinical practice, the preoperative fasting time should be shortened before pancreatic procedures.
AUTORES
Maria L SOUZA1, Suely ARIGA1, Denise F BARBEIRO1, Marcel Autran MACHADO2, Marcel C MACHADO1,2 and Heraldo P SOUZA1