HIGHLIGHTS
- There is solid evidence showing associations of NAFLD with extra-hepatic cancer.
- The most reported types of extra-hepatic NAFLD-related cancer are colorectal, gastric, pancreatic, breast, prostate and bladder.
- NAFLD has been demonstrated as an independent risk factor for extra-hepatic cancer.
ABSTRACT – Background –
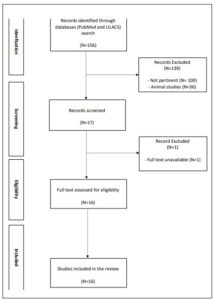
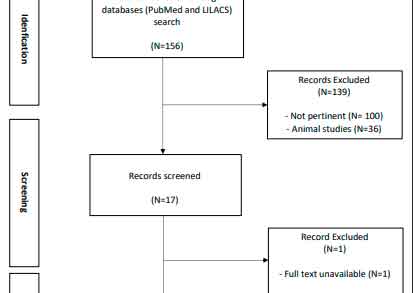
Recently, significant associations between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and extra-hepatic cancer have been reported. Objective – To carry out a comprehensive review of the current evidence in the literature on the association between NAFLD and extrahepatic cancer. Methods – A narrative literature review was performed through an online search for the MeSH terms “fatty liver” and “cancer” in MEDLINE (via PubMed) and LILACS (via BVS). Original studies that described the impact of NAFLD on different types of extra-hepatic malignancies were included. Results – After careful analysis, nine prospective cohort studies, one retrospective cohort study, three case-control studies, and three cross-sectional studies were selected. Conclusion – There is consistent evidence on the association between NAFLD and extra-hepatic carcinogenesis, especially in relation to colorectal, gastric, pancreatic, breast, prostate, and bladder cancers. Keywords – Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; obesity; cancer; carcinogenesis; fatty liver.
AUTORES
Achiles Queiroz Monteiro de REZENDE and Everton CAZZO.